When you encounter the Microsoft AZ-700 exam, don’t rush to find the materials, because there are more important things! Finding new AZ-700 dumps exam questions can help you stand out from the crowd.
The new AZ-700 dumps exam questions 15+ are prepared for you here and are free of charge.
You can also download the new AZ-700 dumps https://www.pass4itsure.com/az-700.html Complete questions 295+, in PDF or VCE format, here to help you score well in the Microsoft Azure AZ-700 exam.
In addition to what has been said above, you should also know where the focus of the exam is.
Where is the focus of preparing for the AZ-700 exam
Some of the topics to consider and focus on when preparing for the AZ-700 exam.
- VNet peering with multiple virtual networks
- Azure Traffic Manager products and features in various SKUs
- Basic knowledge of Azure FrontDoor and WAF products, as well as different SKU offerings
- Azure VPN includes P2S, S2S, and Express Route selections and offers differences
- Azure DNS and the use of Azure Virtual Networks
- Azure Load Balancer and different SKU offerings
- Provision and use of Azure private and service endpoints
These are compiled by me based on my own experience, of course, not necessarily all of them, for reference.
However, it is always beneficial for you to pay attention to these things in your preparation process.
New AZ-600 dumps exam questions to share online
From: Pass4itSure
Number of free AZ-700 questions: 15/295
More Microsoft Azure exam questions….
Question 1:
Your company has two on-premises sites in New York and Los Angeles.
Your company has Azure virtual networks in the East US Azure region and the West US Azure region.
Each on-premises site has Azure ExpressRoute circuits to both regions.
You need to recommend a solution that meets the following requirements:
Outbound traffic to the Internet from workloads hosted on the virtual networks must be routed through the closest available on-premises site.
If an on-premises site fails, traffic from the workloads on the virtual networks to the Internet must reroute automatically to the other site.
What should you include in the recommendation for automatic routing configuration following a failover?
A. Host Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP)
B. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
C. Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
Correct Answer: B
Correct Answer(s):
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) – Microsoft does not support any router redundancy protocols (for example, HSRP, VRRP) for high availability configurations. We rely on a redundant pair of BGP sessions per peering for high availability.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/expressroute/expressroute-routing
Wrong Answers:
Host Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) -Microsoft does not support any router redundancy protocols (for example, HSRP, VRRP) for high availability configurations.
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) -Microsoft does not support any router redundancy protocols (for example, HSRP, VRRP) for high availability configurations.
Question 2:
You have an Azure subscription that contains the following resources:
1.A virtual network named Vnet1
2.Two subnets named subnet1 and AzureFirewallSubnet
3.A public Azure Firewall named FW1
4.A route table named RT1 that is associated with Subnet1
5. A rule routing of 0.0.0.0/0 to FW1 in RT1
After deploying 10 servers that run Windows Server to Subnet1, you discover that none of the virtual machines were activated.
You need to ensure that the virtual machines can be activated.
What should you do?
A. On FW1, create an outbound service tag rule for AzureCloud.
B. On FW1, create an outbound network rule that allows traffic to the Azure Key Management Service (KMS).
C. Deploy a NAT gateway.
D. To Subnet1, associate a network security group (NSG) that allows outbound access to port 1688.
Correct Answer: B
Troubleshoot Azure Windows virtual machine activation problems
Solution
Step 1 Configure the appropriate KMS client setup key
Step 2 Verify the connectivity between the VM and Azure KMS service
This includes:
make sure that the outbound network traffic to the KMS endpoint with the 1688 port is not blocked by the firewall in the VM.
Note:
Understanding Azure KMS endpoints for Windows product activation of Azure Virtual Machines
Azure uses different endpoints for KMS (Key Management Services) activation depending on the cloud region where the VM resides.
Symptom
When you try to activate an Azure Windows VM, you receive an error message resembling the following sample:
Error: 0xC004F074 The Software LicensingService reported that the computer could not be activated. No Key Management Service (KMS) could be contacted. Please see the Application Event Log for additional information.
Cause
Generally, Azure VM activation issues occur if the Windows VM is not configured by using the appropriate KMS client setup key, or the Windows VM has a connectivity problem with the Azure KMS service (kms.core.windows.net, port 1688).
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/firewall/overview
Question 3:
You need to ensure that the owner of VNET3 receives an alert if an administrative operation is performed in the virtual network.
To complete this task, sign in to the Azure portal.
A. See the explanation below.
B. Placeholder
C. Placeholder
D. Placeholder
Correct Answer: A
Monitoring Azure virtual network Alerts Azure Monitor alerts proactively notify you when important conditions are found in your monitoring data. They allow you to identify and address issues in your system before your customers notice them. You can set alerts on metrics, logs, and the activity log.
Create a new alert rule in the Azure portal
Step 1: In the portal, select Monitor > Alerts.
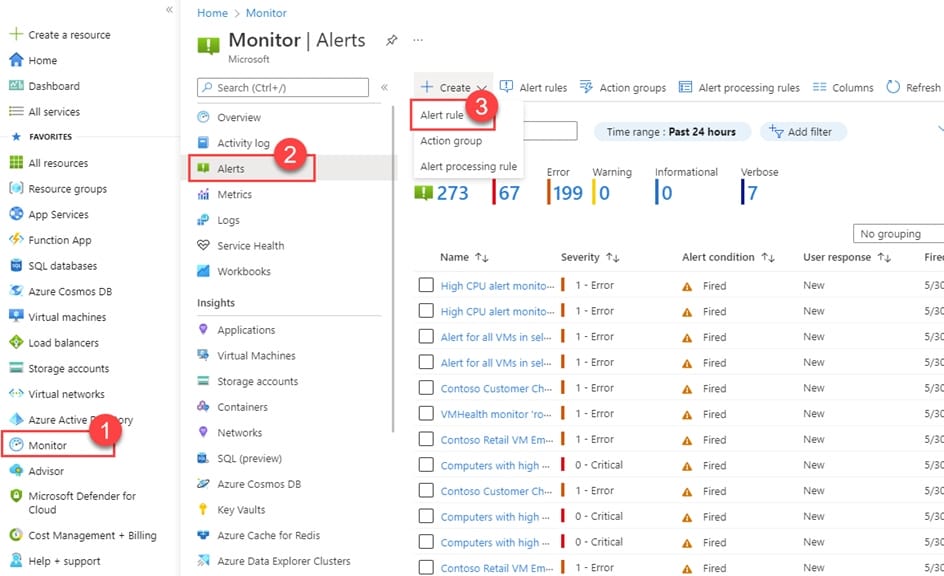
Step 2: Open the + Create menu and select Alert rule.
Step 3: On the Select a resource pane, set the scope for your alert rule. You can filter by subscription, resource type, or resource location. We select Virtual Network.
The Available signal types for your selected resources are at the bottom right of the pane.
Step 4: Select Include all future resources to include any future resources added to the selected scope.
Step 5: Select Done.
Step 6: Select Next: Condition at the bottom of the page.
Step 7: On the Select a signal pane, filter the list of signals by using the signal type and monitor service:
*
Signal type: The type of alert rule you\’re creating. We select the Activity log
*
Monitor service: The service sends the signal. This list is pre-populated based on the type of alert rule you selected. We select Activity log – Administrative (The service that provides the Administrative activity log events)
Step 8: On the Actions tab, select to create the required action group.
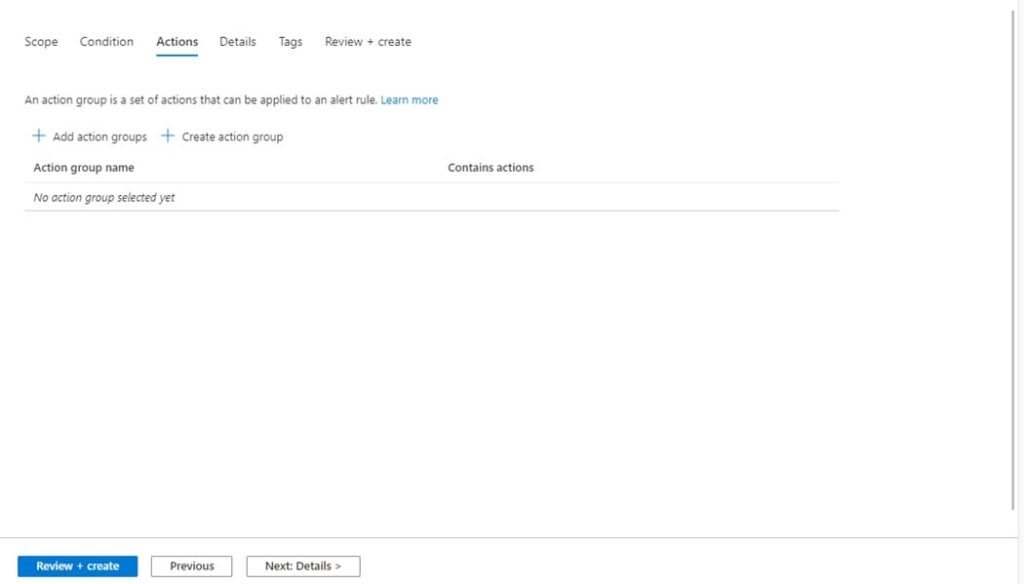
Step 9: Configure basic action group settings
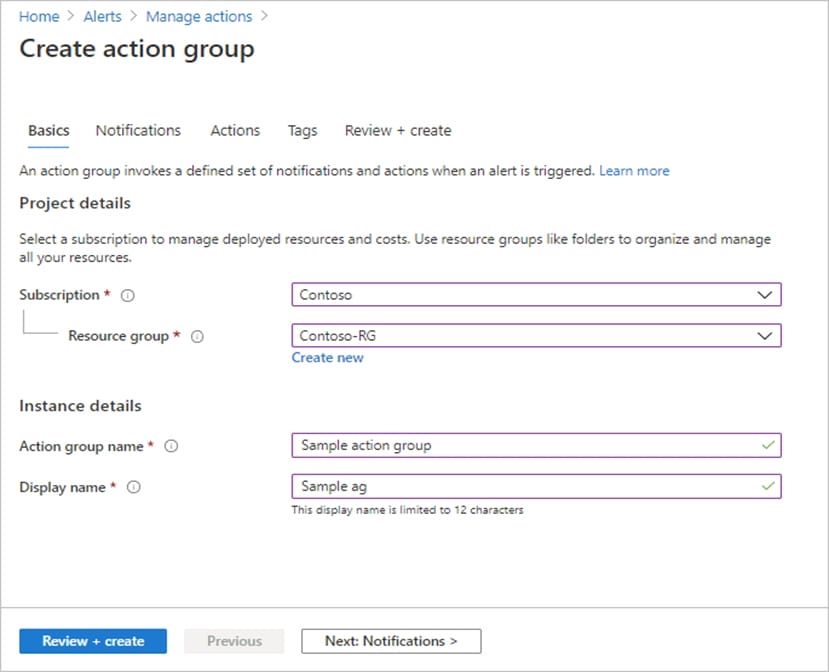
Step 10: Configure notifications. To open the Notifications tab, select Next: Notifications. Alternately, at the top of the page, select the Notifications tab.
Step 11: Define a list of notifications to send when an alert is triggered. Notification: Email Azure Resource Manager Role
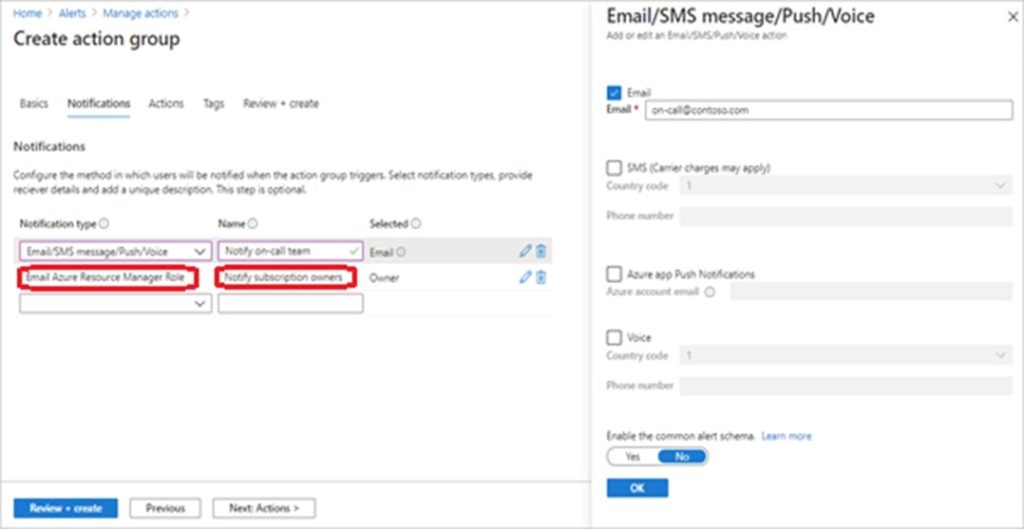
Name: Notify Owner
Step 12: Select OK.
Step 13: Finish the remaining steps in the wizard.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/monitor-virtual-network https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/alerts/alerts-create-new-alert-rule?tabs=metric#create-a-new-alert-rule-in-the-azure-portal
Question 4:
You need to ensure that only hosts on VNET1 can access the storage123456789 storage account. The solution must ensure that access occurs over the Azure backbone network.
To complete this task, sign in to the Azure portal.
A. See the explanation below.
B. Placeholder
C. Placeholder
D. Placeholder
Correct Answer: A
Use private endpoints for Azure Storage You can use private endpoints for your Azure Storage accounts to allow clients on a virtual network (VNet) to securely access data over a Private Link. The private endpoint uses a separate IP address from the VNet address space for each storage account service. Network traffic between the clients on the VNet and the storage account traverses over the VNet and a private link on the Microsoft backbone network, eliminating exposure from the public internet.
Connect to a storage account using an Azure Private Endpoint
Create a private endpoint
Step 1: In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Storage account. Select Storage accounts in the search results.
Step 2: Locate and select the Storage Account storage123456789
Step 3: Select the Networking tab or select Next: Advanced then Next: Networking.
Step 4: In the Networking tab, under Network connectivity select Disable public access and use private access.
Step 5: In Private endpoint, select + Add private endpoint.
Step 6: In Create private endpoint enter or select the following information:
*Details omitted*
* Virtual network: Select VNET1.
Step 7: Select OK.
Step 8: Select Review.
Step 9: Select Create.
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-private-endpoints https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/private-link/tutorial-private-endpoint-storage-portal
Question 5:
You need to ensure that all hosts deployed to subnet3-2 connect to the internet by using the same static public IP address. The solution must minimize administrative effort when adding hosts to the subnet.
To complete this task, sign in to the Azure portal.
A. See the explanation below.
B. Placeholder
C. Placeholder
D. Placeholder
Correct Answer: A
NAT gateway provides outbound internet connectivity for one or more subnets of a virtual network. Once the NAT gateway is associated with a subnet, NAT provides source network address translation (SNAT) for that subnet. NAT gateway
specifies which static IP addresses virtual machines use when creating outbound flows.
Plan:
Stage 1: Create a NAT gateway
Stage 2: Edit subnet subnet3-2 and link it to the NAT gateway
Stage 1: Create a NAT gateway
Step 1: Sign in to the Azure portal.
Step 2: In the search box at the top of the portal, enter NAT gateway. Select NAT gateways in the search results.
Step 3: Select + Create.
Step 4: In Create Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
* NAT gateway name: Enter myNATgateway
Step 5: Select the Outbound IP tab, or select the Next: Outbound IP button at the bottom of the page.
Step 6: In the Outbound IP tab, enter or select the following information:
Public IP addresses – Select Create a new public IP address.
In Name, enter myPublicIP.
Select OK.
Step 7: Select the Review + Create tab, or select the blue Review + Create button at the bottom of the page.
Step 8: Select Create.
Stage 2: Edit subnet subnet3-2 and link it to the NAT gateway
Change subnet settings
Step 1: Go to the Azure portal to view your virtual networks. Search for and select Virtual networks.
Step 2: Select the name of the virtual network containing the subnet you want to change.
Step 3: From Settings, select Subnets.
Step 4: In the list of subnets, select the subnet you want to change settings for. Here choose subnet3-2 connect.
Step 5: On the subnet page, change the NAT Gateway to myNATgateway (the one we created in Stage 1).
Step 6: Select Save.
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/nat-gateway/nat-gateway-resource https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/nat-gateway/quickstart-create-nat-gateway-portal
Question 6:
You need to ensure that you can deploy Azure virtual machines to the France CentralAzure region. The solution must ensure that virtual machines in the France Central region are in a network segment that has an IP address range of 10.5.1.0/24.
To complete this task, sign in to the Azure portal.
A. See the explanation below.
B. Placeholder
C. Placeholder
D. Placeholder
Correct Answer: A
You can create a virtual network before you create a virtual machine or you can create the virtual network as you create a virtual machine.
You create these resources to support communication with a virtual machine:
Network interfaces
IP addresses
Virtual network and subnets
Create a virtual network
Step 1: Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the portal.
Step 2: In the search box, enter Virtual Network. Select Virtual Network in the search results.
Step 3: In the Virtual Network page, select Create.
Step 4: In Create Virtual Network, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
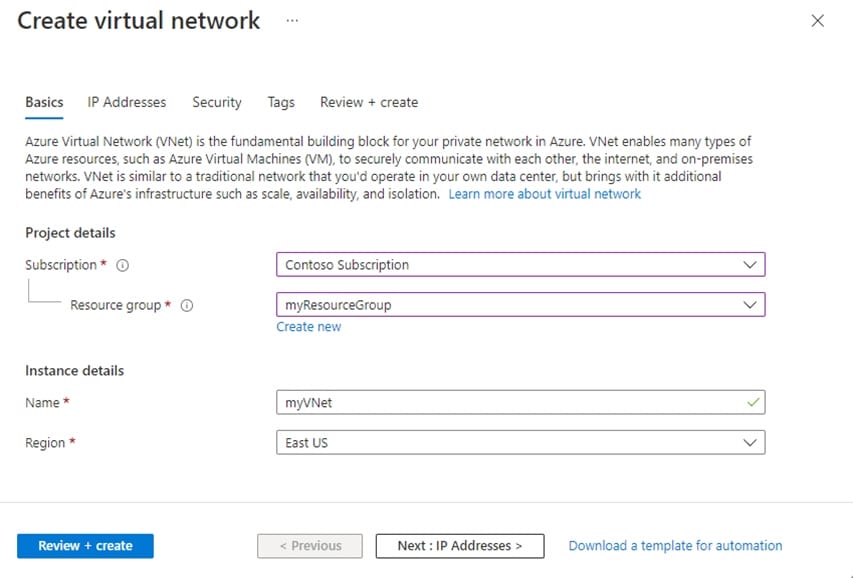
Step 5: Enter Region: France Central
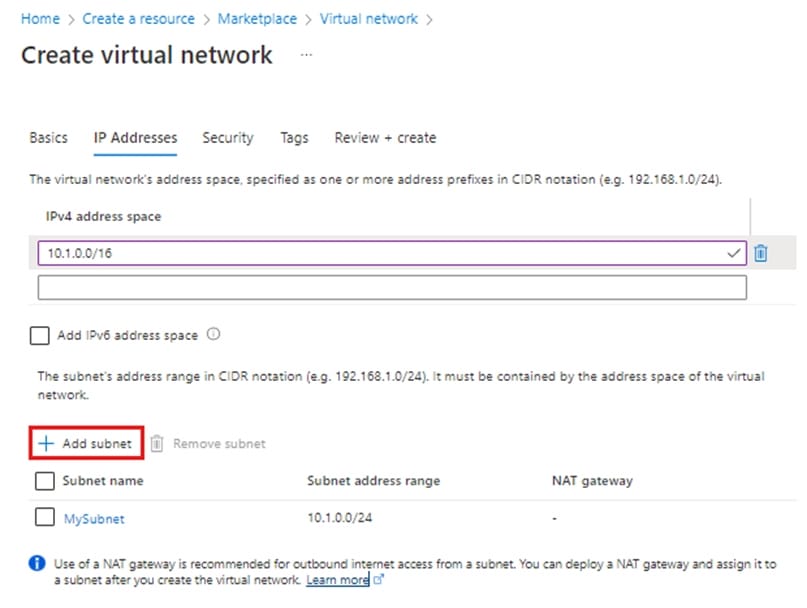
Step 6: Select the IP Addresses tab, or select the Next: IP Addresses button at the bottom of the page and enter the following information then select Add:
Step 7: For IPv4 address space enter: 10.5.1.0/16
Step 8: Click Add Subnet
Step 9: For Subnet address range Enter 10.5.1.0/24.
Step 10: Finish the wizard.
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/quick-create-portal
Question 7:
You have an Azure virtual network named Vnet1 that has one subnet. Vnet1 is in the West Europe Azure region.
You deploy an Azure App Service app named App1 to the West Europe region.
You need to provide App1 with access to the resources in Vnet1. The solution must minimize costs.
What should you do first?
A. Create a private link.
B. Create a new subnet.
C. Create a NAT gateway.
D. Create a gateway subnet and deploy a virtual network gateway.
Correct Answer: B
Create a new subnet, since both Vnet and App Service are in the same region.
Regional VNet Integration = “If the VNet is in the same region, either create a new subnet or select an empty pre-existing subnet”
Question 8:
You have an Azure Front Door instance named FD1 that is protected by using Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF).
FD1 uses a frontend host named app1.contoso.com to provide access to Azure web apps hosted in the East US Azure region and the West US Azure region.
You need to configure FD1 to block requests to app1.contoso.com from all countries other than the United States.
What should you include in the WAF policy?
A. a frontend host association
B. a managed rule set
C. a custom rule that uses a rate limit rule
D. a custom rule that uses a match rule
Correct Answer: C
Question 9:
You need to connect Vnet2 and Vnet3. The solution must meet the virtual networking requirements and the business requirements.
Which two actions should you include in the solution? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
A. On the peering from Vnet1, select Allow for Traffic forwarded from the remote virtual network.
B. On the peerings from Vnet2 and Vnet3, select Allow for Traffic forwarded from a remote virtual network.
C. On the peering from Vnet1, select Use the remote virtual network\’s gateway or Route Server.
D. On the peering from Vnet1, select Allow for Traffic to the remote virtual network.
E. On the peerings from Vnet2 and Vnet3, select Use the remote virtual network\’s gateway or Route Server.
Correct Answer: BE
The correct answer is: BE.
The justification is as follows:
-E IS an answer because without it the requirements cannot be met.
– D is NOT an answer, because: The case study says that “There is bidirectional peering between Vnet1 and Vnet2. There is bidirectional peering between Vnet1 and Vnet3.” This means that “Traffic to remote virtual network” is already allowed for Vnet1<…>Vnet2 and Vnet1<…>.
-C is a total nonsense.
-B IS an answer because Vnet1 contains the VPN gateway that forwards the traffic between Vnet2 and Vnet3.
-A is NOT an answer, because Vnet2 and Vnet3 don’t have VPN gateways so they cannot forward traffic to Vnet1. Documentation: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-network-manage-peering?tabs=peering-portal#create-a-peering https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-about-vpngateways
Question 10:
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure subscription that contains the route tables and routes shown in the following table.
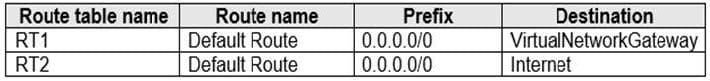
The subscription contains the subnets shown in the following table.
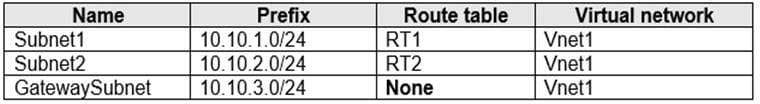
The subscription contains the virtual machines shown in the following table.
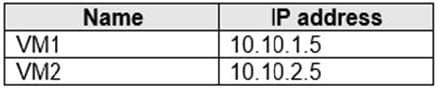
There is a Site-to-Site VPN connection to each local network gateway.
For each of the following statements, select Yes of the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Correct Answer:

Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-network/virtual-networks-udr-overview
Question 11:
You are configuring two network virtual appliances (NVAs) in an Azure virtual network. The NVAs will be used to inspect all the traffic within the virtual network.
You need to provide high availability for the NVAs. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you include in the solution?
A. Azure Standard Load Balancer
B. Azure Application Gateway
C. Azure Traffic Manager
D. Azure Front Door
Correct Answer: A
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/reference-architectures/dmz/nva-ha?tabs=cli
Question 12:
You have Azure virtual machines in three Azure regions.
Each virtual machine has a public IP address assigned to its network interface. An application named App1 is installed in each virtual machine.
You plan to implement Azure Front Door-based load balancing across all the virtual machines.
You need to ensure that App1 on the virtual machines will only accept traffic routed from Azure Front Door.
What should you implement?
A. Azure Private Link
B. Service endpoints
C. Network security groups (NSGs) with service tags
D. Network security groups (NSGs) with application security groups
Correct Answer: C
Correct Answer(s):
Network security groups (NSGs) with service tags – To lock down your application to accept traffic only from your specific Front Door, you will need to set up IP ACLs for your backend and then restrict the traffic on your backend to the specific
value of the header \’X-Azure-FDID\’ sent by Front Door. These steps are detailed below:
Configure IP ACLing for your backends to accept traffic from Azure Front Door\’s backend IP address space and Azure\’s infrastructure services only.
The above step means configuring NSGs with service tags.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/frontdoor/front-door-faq
Wrong Answers:
Azure Private Link – Azure Private Link enables you to access Azure PaaS Services over a private endpoint in your
virtual network.
Service endpoints – The service endpoint provides secure and direct connectivity to Azure services over an optimized route over the Azure backbone network. It does not restrict traffic.
Network security groups (NSGs) with application security groups – ASGs \’s allow you to group virtual machines and define network security policies based on those groups. You must also use the service tag AzureFrontDoor.The backend in the network security group restricts the traffic.
Question 13:
You plan to implement an Azure application gateway in the East US Azure region. The application gateway will have a Web Application Firewall (WAF) enabled.
You need to create a policy that can be linked to the planned application gateway. The policy must block connections from IP addresses in the 131.107.150.0/24 range. You do NOT need to provision the application gateway to complete this task.
To complete this task, sign in to the Azure portal.
A. See the explanation below.
B. Placeholder
C. Placeholder
D. Placeholder
Correct Answer: A
Web Application Firewall Policies contain all the WAF settings and configurations. This includes exclusions, custom rules, managed rules, and so on. These policies are then associated with an application gateway (global), a listener (per-site),
or a path-based rule (per-URI) for them to take effect.
Part 1: Create a WAF policy
Create a basic WAF policy with a managed Default Rule Set (DRS) using the Azure portal.
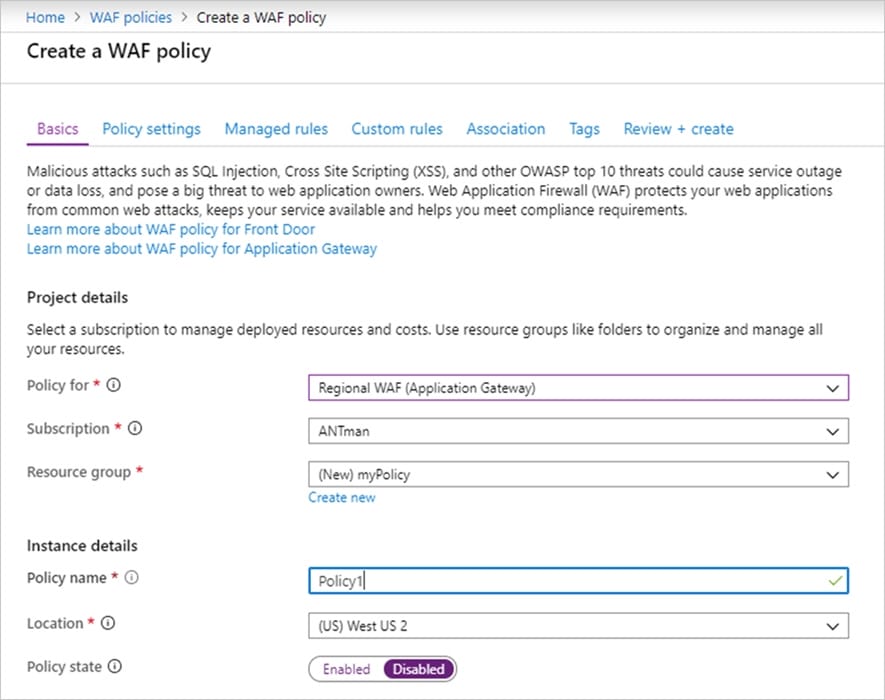
Step 1: On the upper left side of the portal, select Create a resource. Search for WAF, select Web Application Firewall, then select Create.
Step 2: On Create a WAF policy page, Basics tab, enter or select the following information and accept the defaults for the remaining settings:
Policy for – Regional WAF (Application Gateway)
Subscription – Select your subscription name
Resource group – Select your resource group
Policy name – Type a unique name for your WAF policy.
Location: East US
Step 3: On the Association tab, select Add association, then select one of the following settings:
Setting – Value
Application Gateway- Select the application gateway, and then select Add.
HTTP Listener – Select the application gateway, select the listeners, and then select Add.
Route Path – Select the application gateway, select the listener, select the routing rule, and then select Add.
Step 4: Select Review + Create, then select Create.
Part 2: Configure WAF rule
When you create a WAF policy, by default it is in Detection mode. In Detection mode, WAF doesn\’t block any requests. Instead, the matching WAF rules are logged in the WAF logs. To see WAF in action, you can change the mode settings to
Prevention. In Prevention mode, matching rules defined in the CRS Ruleset you selected are blocked and/or logged in the WAF logs.
Custom rules
Step 5: To create a custom rule, select Add custom rule under the Custom rules tab.
This opens the custom rule configuration page.
Step 6: On the Add custom rule page, use the following test values to create a custom rule:
Setting – Value
Custom rule name – AnyName
Status – Enabled
Rule type- Match
Priority – 100
Match type- IP address
Match variable – SocketAddr (for example)
Operation – Does contain
IP address or range – 131.107.150.0/24
Then Deny traffic

Step 7: Select Add.
Step 8: Select Next: Association.
Step 9: Select Associate a WAF policy.
Step 10: For WAF policy, select your WAF policy.
Step 11: For Domain, select the domain.
Step 12. Select Add.
Step 13: Select Review + Create.
Step 14: After your policy validation passes, select Create.
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/web-application-firewall/ag/create-waf-policy-ag
Question 14:
You have an Azure subscription.
You plan to implement Azure Virtual WAN as shown in the following exhibit.
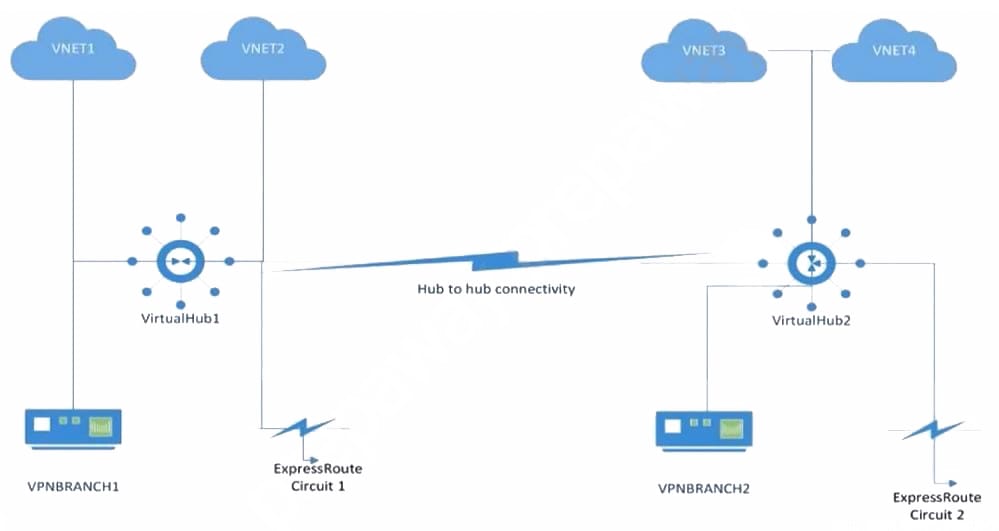
What is the minimum number of route tables that you should create?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 6
Correct Answer: B
Consider the following when configuring Virtual WAN routing:
*
All branch connections (Point-to-site, Site-to-site, and ExpressRoute) need to be associated to the Default route table. That way, all branches will learn the same prefixes.
*
Etc.
Note: The routing capabilities in a virtual hub are provided by a router that manages all routing between gateways using Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). A virtual hub can contain multiple gateways such as a Site-to-site VPN gateway, ExpressRoute gateway, Point-to-site gateway, and Azure Firewall. This router also provides transit connectivity between virtual networks that connect to a virtual hub and can support up to an aggregate throughput of 50 Gbps. These routing capabilities apply to Standard Virtual WAN customers.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-wan/about-virtual-hub-routing
Question 15:
You need to ensure that the URL is accessible through the application gateway.
To achieve the requirement, you add a rewrite rule for the host header.
Did you achieve the requirement?
A. Yes
B. No
Correct Answer: B
Rewrites are not supported when the application gateway is configured to redirect the requests.
More Microsoft exam questions are here.
Here, not only the new AZ-700 exam questions are shared, but also the intimate preparation of what you want.
Prepared a summary of AZ-700 exam resources:
The following resources, which I think must be seen through the AZ-700 exam, come in a variety of forms to meet your different needs.
Document type:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/administer-infrastruct-resources-in-azure/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/paths/azure-fundamentals/
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure-stack/asdk/asdk-troubleshooting?view=azs-2306
- https://github.com/Azure-Samples/Azure-Stack-Hub-Foundation-Core/tree/master/ASF-Training
- https://github.com/Azure-Samples/Azure-Stack-Hub-Foundation-Core/tree/master/ASF-Training/ASF-slides
- Exam AZ-700: Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions – Certifications
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Network Engineer Associate – Certifications
Video type
- Preparing for AZ-700 – Design and implement core networking infrastructure (1 of 5)
- Preparing for AZ-700: Design, implement, and manage connectivity services (2 of 5)
- Preparing for AZ-700: Design and implement application delivery services (3 of 5)
- Preparing for AZ-700: Design and implement private access to Azure services (4 of 5)
- Preparing for AZ-700: Secure network connectivity to Azure resources (5 of 5)
Book type
- Exam Ref AZ-700 Designing and Implementing Microsoft Azure Networking Solutions
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud Solutions
- Building microservices applications on Microsoft azure: designing, Developing, Deploying, and Monitoring
Please note that the AZ-700 exam has been updated!
Latest official news: The exam has been updated on April 25, 2024.
This means that you need to pass the exam promptly, and you must ensure that your new AZ-600 dumps materials are up to date to be effective.
Skills:
- Design and implement core networking infrastructure (25–30%)
- Design, implement, and manage connectivity services (20–25%)
- Design and implement application delivery services (15–20%)
- Design and implement private access to Azure services (10–15%)
- Design and implement Azure network security services (15–20%)
For specific changes, please click here for details.
What are the advantages of passing the Microsoft AZ-700 exam?
- Earning Microsoft Certified for your skills is an excellent addition to your profile.
- Gain sought-after technical skills and a high salary.
Conclusion:
We hope this article helped you pass the AZ-700 exam and shared useful study resources for the exam including new AZ-700 dumps exam questions.
Then again, when you come across the Microsoft AZ-700 exam, the first thing must be to go and download the new AZ-700 dump exam questions, which will help your exam.
Download the new AZ-700 dumps now https://www.pass4itsure.com/az-700.html in PDF or VCE format, Stand out from the crowd.